DIGITAL SIGNALS
In addition to being represented by an analog signal, information can also be represented by a digital signal. For example, a 1 can be encoded as a positive voltage and a 0 as zero voltage. A digital signal can have more than two levels. In this case, we can send more than 1 bit for each level.
Topics discussed in this section:
- Bit Rate
- Bit Length
- Digital Signal as a Composite Analog Signal
- Application Layer
Two digital signals: one with two signal levels and the other with four signal levels
Bit Rate
- Most digital signals are non-periodic, and thus period and frequency are not appropriate characteristics.
- Another term-bit rate (instead of frequency)-is used to describe digital signals.
- The bit rate is the number of bits sent in Is, expressed in bits per second (bps).
Bit Length
- The bit length is the distance one bit occupies on the transmission medium.
- Bit length = propagation speed x bit duration
Digital Signal as a Composite Analog Signal
- Based on Fourier analysis, a digital signal is a composite analog signal.
- A digital signal, in the time domain, comprises connected vertical and horizontal line segments.
- Fourier analysis can be used to decompose a digital signal.
- If the digital signal is periodic, which is rare in data communications, the decomposed signal has a frequency domain representation with an infinite bandwidth and discrete frequencies.
- If the digital signal is non-periodic, the decomposed signal still has an infinite bandwidth, but the frequencies are continuous.
The time and frequency domains of periodic and nonperiodic digital signals
A digital signal is a composite analog
signal with an infinite bandwidth.
Transmission of Digital Signals
- We can transmit a digital signal by using one of two different approaches: base-band transmission or broadband transmission.
- Base-band transmission means sending a digital signal over a channel without changing the digital signal to an analog signal.
- Broadband transmission or modulation means changing the digital signal to an analog signal for transmission.
Base-band transmission
Base-band transmission of a digital
signal that preserves the shape of the
digital signal is possible only if we have
a low-pass channel with an infinite or
very wide bandwidth.
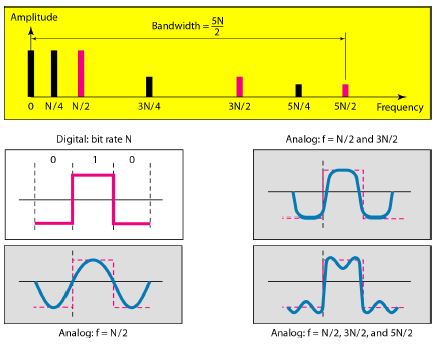
Rough approximation of a digital signal using the first harmonic for worst case
Simulating a digital signal with first three harmonics
In base-band transmission, the required
bandwidth is proportional to the bit rate;
if we need to send bits faster, we need
more bandwidth.
Bandwidth requirements
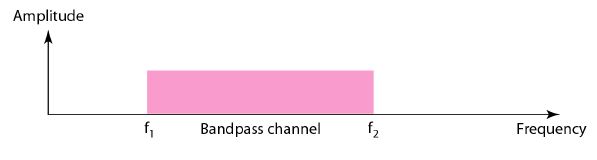
Bandwidth of a band-pass channel
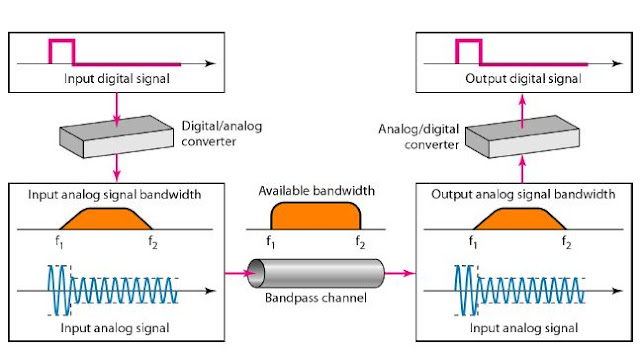
If the available channel is a band-pass
channel, we cannot send the digital
signal directly to the channel;
we need to convert the digital signal to
an analog signal before transmission.
Modulation of a digital signal for transmission on a band-pass channel