CIRCUIT-SWITCHED NETWORKS
A circuit-switched network consists of a set of switches connected by physical links. A connection between two stations is a dedicated path made of one or more links. However, each connection uses only one dedicated channel on each link. Each link is normally divided into n channels by using FDM or TDM.
Topics discussed in this section:
- Three Phases
- Efficiency
- Delay
- Circuit-Switched Technology in Telephone Networks
Note
A circuit-switched network is made of a
set of switches connected by physical
links, in which each link is
divided into n channels.
A trivial circuit-switched network
Switching Process
- When end system Sender needs to communicate with end system Receiver, Sender needs to request a connection to Receiver that must be accepted by all switches as well as by Receiver itself.Then an acknowledgment from receiver needs to be sent in the opposite direction to sender. Only after sender receives this acknowledgment is the connection established. This is called the setup phase;
- A circuit (channel) is reserved on each link, and the combination of circuits or channels defines the dedicated path. After the dedicated path made of connected circuits (channels) is established, data transfer can take place.
- After all data have been transferred, the circuits are tear down.
Note
In circuit switching, the resources need
to be reserved during the setup phase;
the resources remain dedicated for the
entire duration of data transfer until the
teardown phase.
Efficiency
Circuit Switching is not as efficient as the other two types of networks because resources are allocated during the entire duration of the connection.
It is good for Telephone Network.However it is not well for Computer communication.
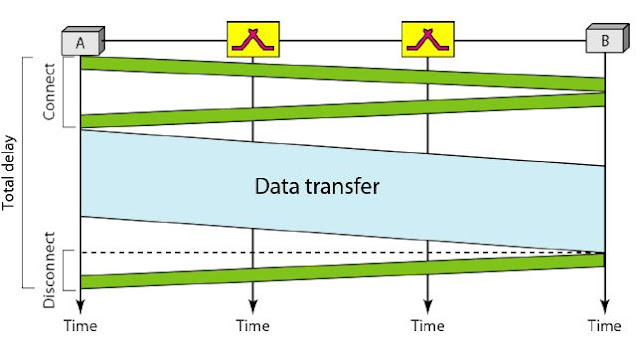
Delay
Although a circuit-switched network normally has low efficiency, the delay in this type of network is minimal. During data transfer the data are not delayed at each switch; the resources are allocated for the duration of the connection.
Delay in a circuit-switched network
Note
Switching at the physical layer in the
traditional telephone network uses
the circuit-switching approach.